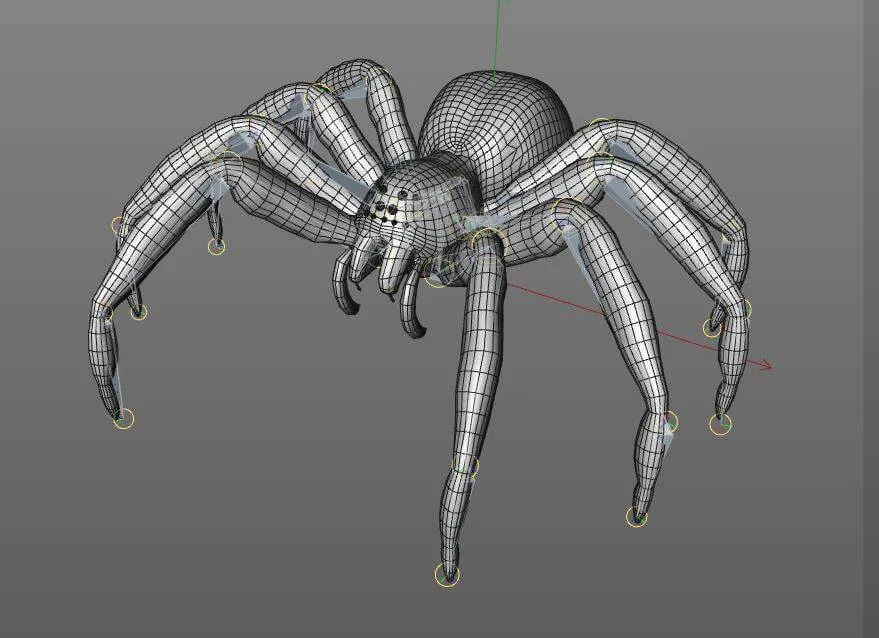
What is a 3D Tarantula View
A 3D tarantula view offers a unique and immersive perspective on these fascinating creatures. Unlike traditional images or videos, 3D technology allows you to perceive the tarantula’s form, structure, and movements in three dimensions. This can greatly enhance your understanding and appreciation of their complex anatomy and behavior. By utilizing specialized viewing methods like 3D glasses or virtual reality, viewers can explore the tarantula from various angles, gaining a deeper insight into its physical characteristics and how it interacts with its environment. This technology is becoming increasingly popular among enthusiasts and scientists alike, providing new ways to study and learn about these intriguing arachnids. This innovative approach is a fantastic way to bring the world of tarantulas to life.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Tarantula
Understanding tarantula anatomy is key to appreciating a 3D view. Tarantulas, like all spiders, have a body divided into two main parts the cephalothorax (fused head and thorax) and the abdomen. The cephalothorax houses the tarantula’s brain, mouthparts, eyes, and legs, while the abdomen contains the digestive and reproductive organs. They also have a rigid exoskeleton made of chitin, which provides protection and support. Their bodies are covered in sensory hairs, which detect vibrations, air currents, and other environmental stimuli. Learning the parts can make a 3D view a lot more interesting and allow for a more intimate view of the anatomy.
Key Body Parts to Observe in 3D

When viewing a tarantula in 3D, pay special attention to the following: The chelicerae (fangs), which are used for injecting venom and manipulating prey; the pedipalps, which are used for sensing, mating, and manipulating food; the eight legs, which are used for locomotion; and the spinnerets, which produce silk for web-making and other purposes. In 3D, you can appreciate the intricate details of the tarantula’s body shape, including the arrangement of hairs, the texture of the exoskeleton, and the structure of its eyes. These details are often lost in two-dimensional images and are crucial for understanding the spider’s adaptations to its environment and its lifestyle. A tarantula in 3D will allow for a more in-depth look at these parts.
The Benefits of Seeing a Tarantula in 3D
Viewing a tarantula in 3D offers numerous benefits. It provides a more realistic and immersive experience, allowing viewers to better understand the tarantula’s size, shape, and movements. This enhanced perspective can be particularly useful for educational purposes, providing a clearer understanding of the spider’s anatomy and behavior. Additionally, 3D viewing can enhance the aesthetic appreciation of tarantulas, highlighting the intricate details of their bodies and the beauty of their patterns and colors. Furthermore, 3D models can be used for scientific research, allowing scientists to study the spiders from different angles, and examine their structural components.
Enhanced Understanding of Spider Morphology
3D views significantly enhance our understanding of spider morphology. By observing a tarantula in three dimensions, we can better grasp its structural complexity. The exoskeleton, the arrangement of hairs, and the positioning of limbs become much clearer, allowing for a deeper understanding of how these features contribute to the spider’s survival. This in-depth perspective is especially valuable for entomologists and arachnologists, aiding in the identification and classification of species and offering deeper insights into how morphology influences behavior and ecological roles. 3D viewing technologies provide opportunities for learning.
Improved Appreciation for Tarantula Biology

Viewing tarantulas in 3D improves our appreciation of their complex biology. The technology allows us to explore aspects of their life, from hunting strategies to their methods of protection. The intricate details of their fangs, the texture of their exoskeletons, and the structure of their eyes become more apparent, providing a fuller understanding of their adaptations to their environment. This increased appreciation leads to a better understanding of their roles in ecosystems. For those fascinated by the natural world, 3D views offer a compelling way to connect with these creatures on a deeper level.
Top 7 Amazing Facts About Tarantulas in 3D
Fact 1 Eyesight Capabilities
Tarantulas have eight eyes, arranged in two rows. They don’t have great eyesight, but can still see movement and shadows, which is useful for hunting. In 3D, you can better see how these eyes are positioned on their cephalothorax, and how they provide a wide field of vision. This unique view helps highlight the limitations of their sight, such as their inability to see fine details, and the adaptations they employ to compensate, such as the use of vibrations and sensory hairs.
Fact 2 Exoskeleton Structure
The exoskeleton of a tarantula is composed of chitin, which provides protection and support. The 3D view allows you to appreciate the exoskeleton’s intricate structure, including the patterns, grooves, and the arrangement of hairs. This provides a deeper insight into how the exoskeleton functions, protecting the spider from predators and providing a surface for muscle attachment. In a 3D view, the texture of the exoskeleton becomes more vivid, highlighting its role in the tarantula’s survival.
Fact 3 Movement and Locomotion
Tarantulas are known for their varied methods of movement, including walking, climbing, and sometimes even jumping. A 3D view can showcase how their eight legs work in unison to move, whether they are traversing rough terrain or scaling vertical surfaces. These views highlight the tarantula’s agility and precision, and also allow viewers to better understand how the structure of their legs and the texture of their feet enable them to grip surfaces effectively. Furthermore, this shows how each leg plays a unique role in the spider’s movement.
Fact 4 Hunting Strategies
Tarantulas are ambush predators, lying in wait for prey. In 3D, you can better understand their hunting strategies, including how they use their fangs and venom to subdue their prey. The 3D view can also highlight the sensory hairs on their legs, which detect vibrations. These are used to sense the presence of potential prey. This perspective emphasizes their use of ambush tactics, and highlights the adaptations that make them effective hunters. Observing their hunting methods in 3D provides a more intimate view of their survival.
Fact 5 Venom Delivery

Tarantulas use their fangs to inject venom, which paralyzes or kills their prey. In 3D, you can examine the structure of the fangs and see how they penetrate the prey. The 3D view also allows you to analyze the tarantula’s venom glands and how they release the venom. This immersive view highlights the tarantula’s ability to inject venom, and it provides a better understanding of their defensive mechanism.
Fact 6 Moulting Process
Tarantulas shed their exoskeletons to grow, a process known as molting. In 3D, you can observe the details of the new exoskeleton. This technology helps to visualize the delicate process of shedding the old exoskeleton and how the tarantula emerges with a new, larger one. This reveals how the tarantula’s body expands within the old exoskeleton. The 3D view can also highlight the adaptations that allow them to survive this vulnerable period.
Fact 7 Habitat and Environment
Tarantulas inhabit various environments, from tropical rainforests to deserts. A 3D view can help you see them in their natural habitat. This provides a better understanding of how their adaptations help them survive. These views often showcase the tarantula’s behavior, and the ways it interacts with other organisms in its environment. The 3D view enhances this understanding, showing the complex relationships between the spider and its surroundings.
How 3D Technology Enhances Tarantula Viewing
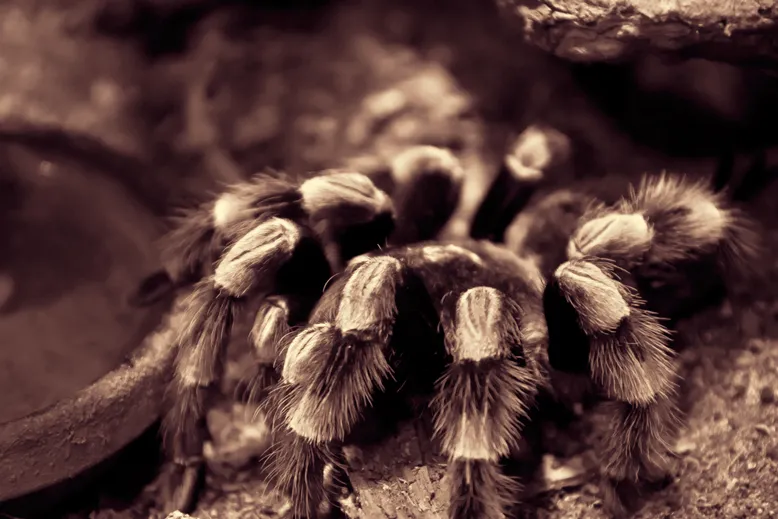

Different 3D Viewing Methods
Several methods enable 3D viewing of tarantulas. These include the use of stereoscopic glasses that present a slightly different image to each eye, creating the illusion of depth. Virtual reality (VR) headsets provide a fully immersive experience, allowing viewers to explore tarantula models from all angles. Advanced techniques, such as 3D scanning and modeling, are also used to create detailed digital representations of tarantulas. These methods allow for more interactive and engaging ways to study tarantulas.
Where to Find 3D Tarantula Resources
Numerous resources are available for viewing tarantulas in 3D. Online platforms offer 3D models, videos, and interactive experiences. Museums and science centers are also adopting 3D technology to display tarantulas and other arachnids. Scientific journals and research publications are increasingly using 3D images and models to present their findings. For anyone interested in exploring tarantulas in 3D, these resources provide an exciting way to learn and discover more about these fascinating creatures.
Conclusion
Viewing tarantulas in 3D offers a unique and engaging way to appreciate these amazing creatures. The technology enhances our understanding of their anatomy, behavior, and ecological roles. Through 3D viewing, we can gain a greater appreciation for the tarantulas. This immersive approach allows for a deeper connection to these animals, and highlights their importance in our world. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for exploring the world of tarantulas in 3D will only increase, leading to new discoveries and a greater appreciation for these fascinating arachnids.
