What are Tarantula Bites
Tarantulas, large, hairy spiders belonging to the Theraphosidae family, are often misunderstood. While their size can be intimidating, their bites are rarely life-threatening to humans. These arachnids, found in various habitats worldwide, use their fangs to inject venom into prey. When a tarantula bites a human, it’s usually a defensive reaction, often triggered by perceived threats like being handled or accidentally stepped on. Understanding the nature of tarantula bites is the first step toward dispelling myths and promoting informed perspectives on these fascinating creatures. Most bites are not serious, but it’s important to know how to react.
Symptoms of Tarantula Bites
The symptoms of a tarantula bite can vary based on several factors, including the species of the tarantula, the amount of venom injected, and the individual’s sensitivity. Most bites result in mild discomfort, similar to a bee sting. However, it’s essential to monitor for any adverse reactions and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen. Paying close attention to the specific symptoms can help determine the severity of the bite and guide appropriate treatment. Knowing what to expect is critical for managing the situation effectively.
Mild Symptoms
Mild symptoms are the most common outcome of a tarantula bite. These may include immediate pain at the bite site, which can feel like a pinprick or a sharp sting. Redness, swelling, and itching around the bite area are also typical. These symptoms usually subside within a few hours or days. In some cases, there might be minor muscle cramps or a slight headache. These mild reactions are generally manageable with home care, such as cleaning the area and applying a cold compress.
Moderate Symptoms
Moderate symptoms are less frequent but can occur, especially if the individual is sensitive to the venom. These symptoms might include increased pain and swelling, along with a noticeable increase in redness. Some individuals might experience nausea, vomiting, or dizziness. Muscle cramps can become more intense and prolonged. It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms closely. If moderate symptoms develop, medical advice from a professional is advisable to prevent complications.
Severe Symptoms
Severe symptoms are rare but can indicate a serious reaction. Signs of a severe reaction include difficulty breathing, severe swelling, chest pain, or a rapid heartbeat. In extreme cases, anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction, can occur. If severe symptoms develop, immediate medical attention is crucial. Call emergency services immediately and describe the situation to the medical personnel. These symptoms are a sign that professional intervention is required without delay.
Are Tarantula Bites Venomous?
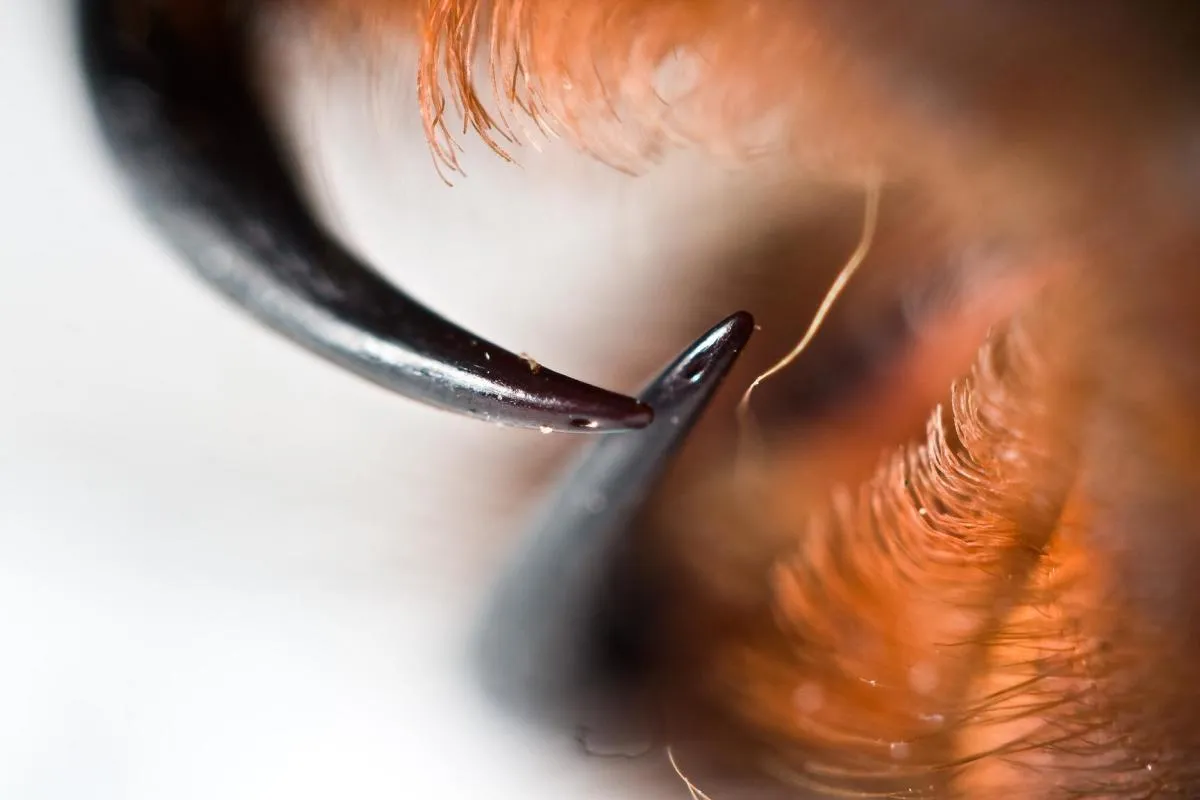
Yes, tarantulas are venomous. They possess fangs that inject venom into their prey to immobilize and digest them. However, the potency of tarantula venom is generally low, posing little threat to humans. The venom is designed to affect insects and small animals, not humans. The effects of the venom on humans are usually localized, causing pain and swelling around the bite site. While tarantula bites are venomous, they are not typically considered dangerous. In most cases, the effects are similar to those of a bee sting and are manageable with basic care.
How to Treat a Tarantula Bite
Treating a tarantula bite involves different approaches depending on the severity of the symptoms. For mild cases, home treatment is usually sufficient. However, if symptoms escalate or the individual exhibits severe reactions, medical attention becomes essential. Knowing how to respond to the bite effectively can help mitigate potential complications. Prompt and appropriate action can ensure a better outcome.
Home Treatment
Home treatment for a tarantula bite is usually adequate for mild cases. Clean the bite area with soap and water to prevent infection. Apply a cold compress to reduce pain and swelling. You can elevate the affected limb to help reduce swelling further. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can alleviate any discomfort. Make sure to monitor the bite site for any worsening of symptoms. It’s important to seek medical attention if symptoms become severe or you suspect an allergic reaction.
Medical Treatment

Medical treatment may be necessary for moderate to severe reactions. A healthcare professional can assess the bite and provide appropriate care. This may involve administering antihistamines to reduce allergic reactions or pain medications for severe pain. In rare cases of severe allergic reactions, epinephrine might be administered. The doctor will monitor the patient’s vital signs and provide supportive care as needed. Medical professionals have the expertise to manage complicated cases. Always seek professional medical help when symptoms appear serious.
Prevention is Key
Preventing tarantula bites is often straightforward. When in areas where tarantulas are known to inhabit, avoid handling them. If you must handle a tarantula, use protective gloves and be extremely cautious. Educate yourself on the local tarantula species and their habitats. Keep your home and surroundings free of clutter to minimize potential hiding places for these spiders. Regularly inspect areas like basements, garages, and storage sheds. Simple steps like these can significantly lower the risk of unwanted encounters and bites.
Myths About Tarantula Bites
Many myths surround tarantula bites, often exaggerating their danger. One common misconception is that tarantula bites are always deadly. In reality, such cases are exceedingly rare. Another myth suggests that all tarantulas are highly aggressive and prone to biting. In fact, most tarantulas are docile and prefer to retreat rather than engage in conflict. Dispelling these myths with accurate information is essential for promoting safety. Understanding the facts about tarantulas will help in creating a safer approach and diminish any unnecessary fear.
In conclusion, while tarantula bites can cause some discomfort, they are rarely dangerous. Knowing the facts and how to respond appropriately can help you stay safe. Practice prevention, understand the symptoms, and seek medical attention when necessary. Enjoying and understanding these magnificent creatures can coexist harmoniously with proper safety.
