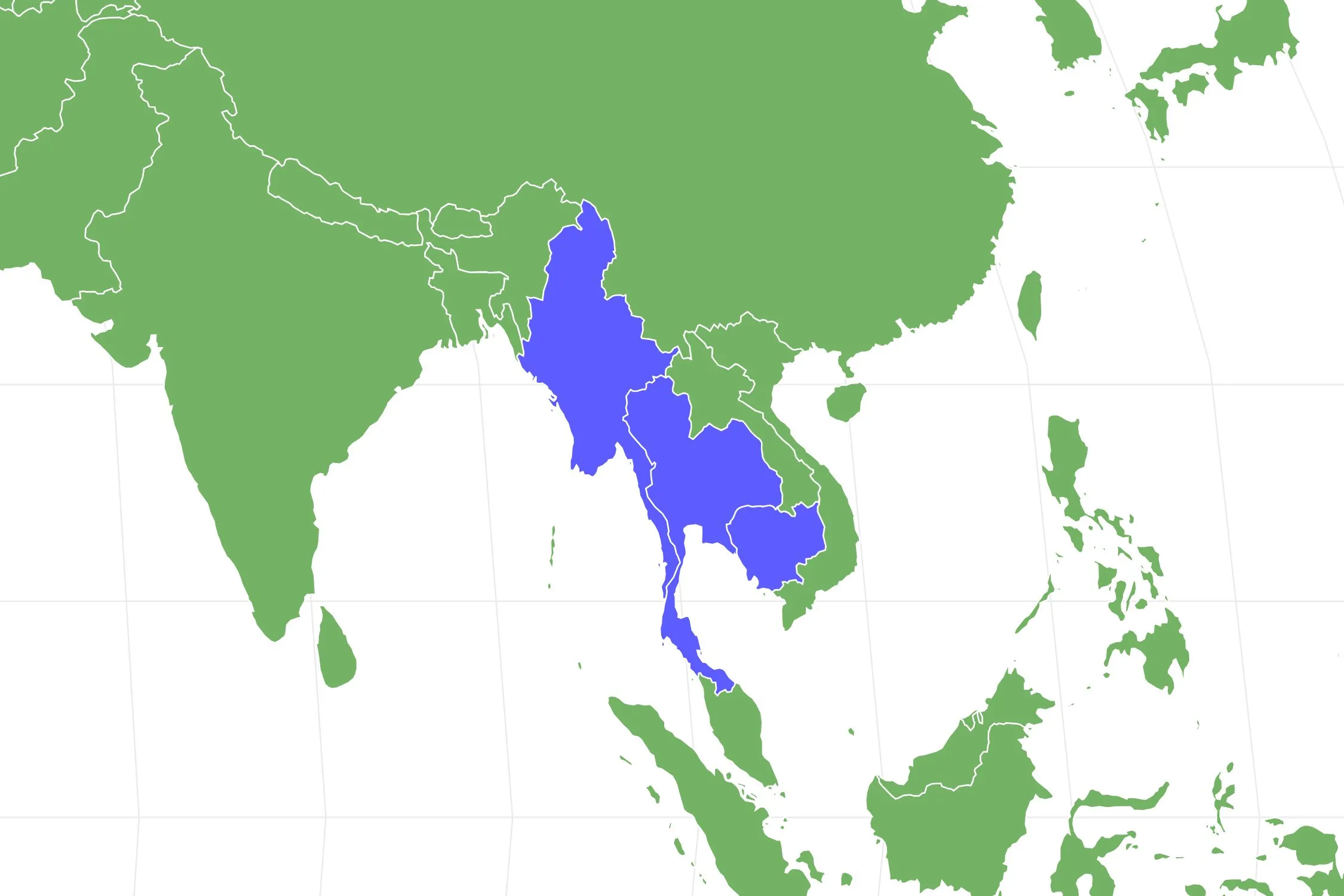
Understanding Tarantula Territory
Tarantulas, fascinating arachnids with a complex social structure, exhibit territorial behavior that dictates their survival and interaction with their environment. Understanding their territory is crucial for both enthusiasts and conservationists. A tarantula territory isn’t merely a space; it’s a carefully selected area that provides essential resources like food, shelter, and opportunities for mating. The size and characteristics of a tarantula’s territory can vary significantly based on species, age, sex, and the surrounding environment. Examining a tarantula territory map reveals how these creatures strategically choose and defend their homes, impacting their chances of thriving in the wild. The study of these maps offers valuable insights into their behavior and conservation needs. Observe how these fascinating creatures have their own world.
Factors Influencing Territory
Several factors play a crucial role in shaping a tarantula’s territory. These include the availability of food sources, the presence of suitable shelter, and the environmental conditions. For instance, a tarantula living in an area with an abundant supply of insects might have a smaller territory compared to one in a resource-scarce environment. The type of habitat, whether it be a forest floor, a desert burrow, or a tree trunk, also impacts the size and nature of the territory. Furthermore, the sex of the tarantula influences territorial behavior, with females often establishing more permanent and defensible territories compared to males, who may roam more widely in search of mates. The map of tarantula territories is, therefore, a dynamic reflection of these multifaceted interactions. This understanding is essential to create a tarantula territory map that accurately reflects their lives.
Habitat and Resources
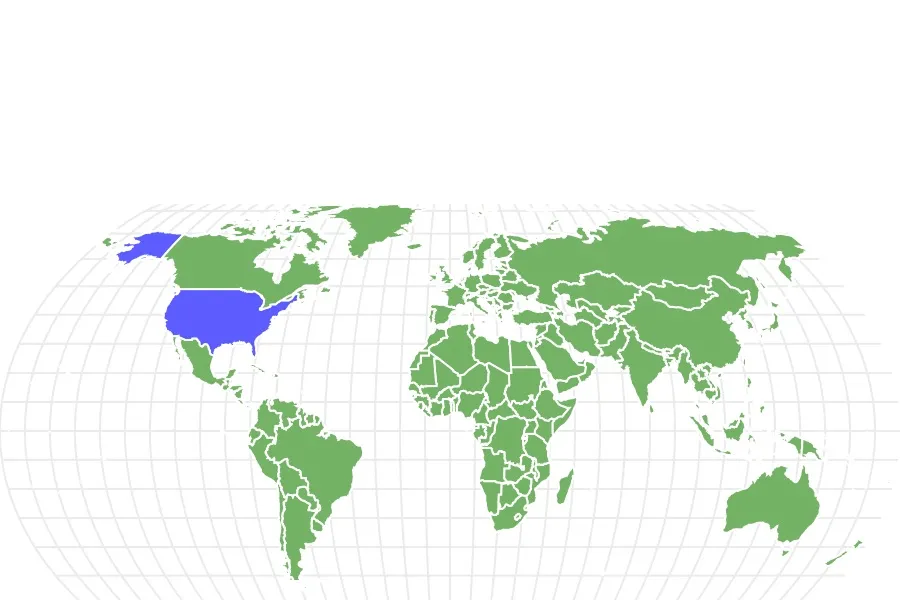
The habitat and available resources within it are fundamental determinants of tarantula territory. Habitats provide shelter from predators and the elements, with burrows, rock crevices, and tree hollows serving as ideal homes. Resources such as insects, small animals, and, occasionally, other arthropods, fuel their survival and reproduction. The distribution of these resources directly influences the size and boundaries of a tarantula’s territory. In areas with limited resources, tarantulas must expand their territory to ensure adequate access to food. Conversely, in environments with a high concentration of prey, they can maintain a smaller, more easily defended territory. The tarantula territory map, therefore, offers a visual representation of these critical relationships between habitat, resources, and the arachnid’s lifestyle.
Top 5 Secrets of Tarantula Territory
Secret 1 Territorial Behavior
Tarantulas are not uniformly aggressive, but they defend their territory when necessary. This behavior varies significantly between species, age, and sex. Some tarantulas display active defense, while others prefer avoidance or passive resistance. The territorial behavior involves a combination of physical displays, like raising their front legs, and, in some cases, the release of urticating hairs or even biting. However, direct conflict is often avoided, with tarantulas primarily aiming to establish dominance through signals and strategic positioning. Understanding these behaviors is crucial for interpreting the tarantula territory map and predicting their interactions within a given habitat. This behavior is a key element of understanding a tarantula’s position on a tarantula territory map.
Secret 2 Environmental Factors

Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and rainfall have a significant impact on tarantula territoriality. Ideal conditions allow tarantulas to thrive within a defined territory. Extremes, such as drought or excessive heat, may force them to alter their territory or seek alternative habitats. For instance, during dry seasons, tarantulas may seek refuge in deeper burrows or areas with higher moisture levels. Understanding how environmental conditions influence tarantula behavior helps researchers predict changes in their distribution and movements, which are crucial elements for creating a tarantula territory map. These adaptations showcase the intricate interplay between the tarantula and its environment.
Secret 3 Resource Availability
The availability of food and water is paramount in dictating the size and characteristics of a tarantula’s territory. A plentiful supply of prey allows a tarantula to maintain a smaller, more easily defended home range. Conversely, scarce resources force these arachnids to expand their search area, potentially leading to overlap with other tarantulas, and changing the tarantula territory map. The abundance of resources also impacts reproductive success, with well-fed females producing more viable eggs. Variations in resource availability due to seasonality or human impact can significantly influence tarantula distribution and territorial behavior. Therefore, the tarantula territory map offers a visual representation of this crucial relationship.
Secret 4 Mating Season
Mating season can dramatically alter the dynamics of tarantula territories. During this period, male tarantulas often abandon their established territories to search for mates. Females, on the other hand, usually remain in their territories, attracting potential partners. This leads to increased movement and interaction between individuals, often resulting in territorial disputes among males. The tarantula territory map reflects this shift, showing the temporary expansion of male territories and the increased activity levels in areas with receptive females. Understanding these seasonal changes is crucial for interpreting the overall patterns of tarantula territoriality. Observing and recording mating patterns is essential in mapping tarantula behavior.
Secret 5 Human Impact

Human activities, such as habitat destruction, pesticide use, and climate change, pose significant threats to tarantula territories. Deforestation and urbanization reduce habitat availability, forcing tarantulas into smaller areas and increasing competition. Pesticides can decimate their food sources, leading to territorial instability. Climate change alters environmental conditions, potentially shifting the distribution of tarantulas and their prey. The tarantula territory map serves as a vital tool for tracking the effects of human impact, identifying vulnerable populations, and guiding conservation efforts. By understanding these threats, we can implement strategies to protect these remarkable creatures. The tarantula territory map is, therefore, a crucial tool.
Mapping Tarantula Habitats
Tools and Techniques
Mapping tarantula territories involves a variety of tools and techniques, ranging from direct observation to sophisticated tracking methods. Traditional methods include visual surveys, where researchers carefully search for tarantulas and their burrows, noting their location and any signs of activity. Advanced techniques involve the use of radio telemetry, GPS tracking, and camera traps to monitor tarantula movements over extended periods. These tools provide valuable data on territory size, home range, and interactions between individuals. Data analysis and mapping software are used to create detailed representations of tarantula territories. The tarantula territory map becomes more detailed as the data grows.
Observation and Data Collection
Effective observation and data collection are crucial to constructing an accurate tarantula territory map. Researchers carefully document various factors, including the location of burrows, the presence of prey, and the behaviors of the tarantulas. The collection of data requires patience and attention to detail, as tarantulas are often secretive and nocturnal. Data is collected over extended periods to account for seasonal variations in behavior and territory size. Analyzing the data, often using mapping software, creates a visual representation of the tarantula territory. It’s important to remember that the tarantula territory map is constantly evolving as new data and knowledge are gained.
Ethical Considerations
When studying tarantula territories, ethical considerations are paramount. Researchers must minimize disturbance to the tarantulas and their habitats. This includes avoiding the disruption of burrows, handling the animals with care, and adhering to all relevant regulations and permits. The well-being of the tarantulas must always take precedence. Additionally, researchers should ensure that their studies contribute to conservation efforts and raise awareness about the importance of protecting these fascinating creatures. Ethical research practices are essential for creating a tarantula territory map that is both scientifically sound and ecologically responsible.
Preserving Tarantula Habitats
Conservation Efforts
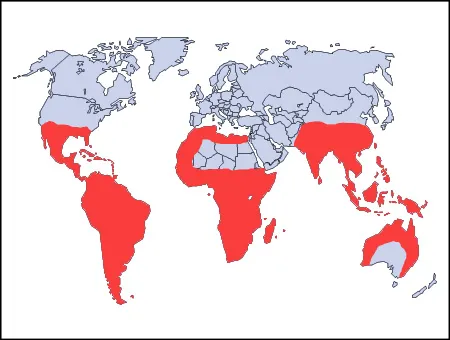
Conservation efforts are critical for protecting tarantulas and their habitats. This involves a multifaceted approach, including habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and public education. Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, safeguards crucial habitats from destruction. Implementing regulations to control the pet trade and prevent illegal collecting is also vital. Furthermore, engaging local communities in conservation efforts can foster a sense of stewardship and encourage sustainable practices. Successful conservation requires collaborative efforts and a commitment to protecting the tarantulas and their habitats, as reflected on the tarantula territory map.
Educating the Public
Educating the public about tarantulas and their importance is essential for conservation. Raising awareness about their ecological roles, threats they face, and the importance of protecting their habitats is a key component. Educational programs, outreach events, and online resources can help to dispel misconceptions and foster appreciation for these fascinating creatures. By promoting a better understanding of tarantulas and their habitats, we can inspire support for conservation efforts and empower individuals to take action. A well-informed public is more likely to advocate for their protection, ensuring the continued presence of tarantulas in their natural environments. The tarantula territory map helps inform this education.