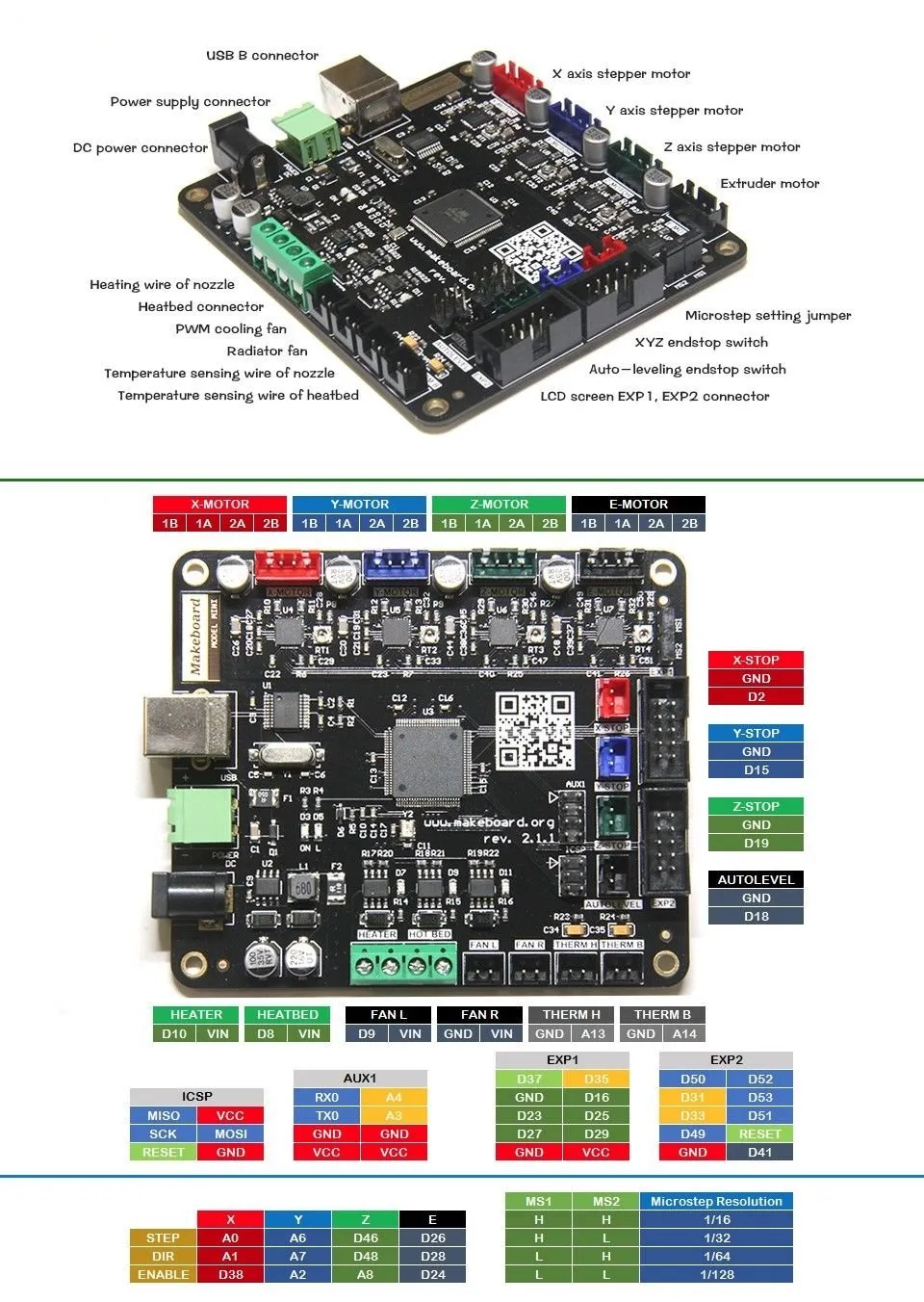
Understanding Tevo Tarantula Slic3r Settings
The Tevo Tarantula is a popular and affordable 3D printer, beloved by hobbyists and beginners alike. However, achieving high-quality prints with the Tevo Tarantula requires careful configuration of its Slic3r settings. Slic3r is a widely-used open-source slicing software that converts 3D models into G-code instructions that your printer can understand. Mastering these settings is crucial for unlocking the full potential of your Tevo Tarantula and producing accurate, detailed, and visually appealing 3D prints. This guide will provide you with the top 5 tips to optimize your Slic3r settings for the Tevo Tarantula, ensuring you get the best possible results.
Why Slic3r Settings Matter
Slic3r settings are the key to controlling every aspect of your 3D printing process. They dictate how the printer moves, how the filament is extruded, and how the layers are built up to create the final object. Incorrect settings can lead to a wide range of issues, from poor layer adhesion and warping to stringing, blobs, and failed prints. Understanding and adjusting these settings allows you to tailor the printing process to the specific characteristics of your filament, the complexity of your model, and the desired print quality. Taking the time to learn and adjust your Slic3r settings will dramatically improve your printing experience.
Key Slic3r Settings for Tevo Tarantula
Several key settings in Slic3r have a significant impact on the quality of your prints. These include print speed, temperature settings, retraction settings, bed adhesion strategies, and filament-specific parameters. Each of these settings interacts with others, making it essential to find a balance that works for your specific setup. This guide will focus on optimizing these key settings, offering practical advice and actionable tips to help you get the best results from your Tevo Tarantula.
Top 5 Tevo Tarantula Slic3r Settings Tips
Tip 1 Bed Leveling Perfection
Proper bed leveling is the foundation of successful 3D printing. A perfectly leveled bed ensures that the first layer of your print adheres properly, preventing warping and ensuring a smooth base for the rest of the print. Using a level bed is the most important part of setting up your printer. An unlevel bed can cause a multitude of printing issues.
Importance of Proper Bed Adhesion
Good bed adhesion is crucial. Without it, the first layer will detach from the bed, leading to a failed print. The first layer needs to be squished onto the bed; this helps it hold to the print surface. Use a brim or a raft if your print has a small footprint. Make sure you are using a glue stick, or any other adhesive, on your print bed, and make sure you are cleaning the bed to avoid oily spots or dust.
Calibration Process
To calibrate your bed, use a piece of paper. Heat up the bed and the nozzle before you level the bed. Make sure you use the paper between the nozzle and the bed. Adjust the bed leveling screws until the nozzle barely scrapes the paper as you move it across the bed. This process might need to be repeated a few times. It is recommended to do it before every print.
Tip 2 Optimal Temperature Configuration
Temperature settings play a critical role in the quality of your prints. The nozzle temperature affects how well the filament melts and extrudes, while the bed temperature impacts the adhesion of the first layer. Experimenting with different temperatures is often necessary to find the optimal settings for your filament. Too low of a temperature will cause the layers not to stick together, and too high of a temperature will cause the filament to ooze.
Nozzle Temperature Guidelines
The nozzle temperature should be determined based on the filament type. PLA typically prints between 190°C and 220°C, ABS between 230°C and 250°C, and PETG between 220°C and 250°C. Refer to the filament manufacturer’s recommendations for the most accurate settings, and always start with the lower end of the range and increase gradually until you achieve optimal results. A temperature tower can be printed to help determine the ideal settings.
Bed Temperature Recommendations
The bed temperature also depends on the filament. For PLA, a bed temperature of 50°C to 60°C is usually sufficient. ABS requires a higher bed temperature, typically between 90°C and 110°C, to prevent warping. PETG usually benefits from a bed temperature of 70°C to 80°C. Ensure the bed is at the correct temperature before the print begins. The bed temperature helps in the adhesion process.
Tip 3 Speed and Acceleration Tuning
Print speed and acceleration settings directly impact the print time and the quality of the final object. Faster speeds can reduce print time, but may also lead to decreased accuracy and more imperfections. Finding the right balance between speed and quality is essential for optimal printing results.
Print Speed Considerations
For the Tevo Tarantula, a print speed of 40-60 mm/s is a good starting point for most filaments. However, the optimal print speed can vary depending on the filament type, the complexity of the model, and the desired print quality. It’s recommended to start with a slower speed and increase it gradually until you observe a decline in print quality.
Acceleration and Jerk Settings
Acceleration and jerk settings control how quickly the printer’s print head changes speed and direction. Higher acceleration and jerk settings can lead to faster prints, but also increase the risk of vibrations and ringing artifacts. Experiment with these settings to find the optimal balance between speed and print quality, and make sure your printer is stable when using it. Be careful when increasing these settings to avoid quality issues.
Tip 4 Filament Selection and Settings
The type of filament you use significantly impacts your Slic3r settings. Different filaments, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and others, have different melting points, require different bed temperatures, and exhibit varying properties. Choosing the right filament and configuring your Slic3r settings accordingly is crucial for successful printing.
PLA, ABS, and PETG Settings

PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a beginner-friendly filament known for its ease of use and low warping. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a more durable filament, but it requires higher temperatures and is more prone to warping. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) offers a good balance of strength, flexibility, and ease of printing. Each filament has its strengths and weaknesses.
Filament Diameter and Flow Rate
Make sure your filament diameter is set correctly in Slic3r. Common filament diameters are 1.75mm and 2.85mm. Also, make sure the flow rate is accurate, a slightly higher flow rate will make the prints more solid. The flow rate should be adjusted based on the filament type and the results of the print. Use a calibration cube to check the settings.
Tip 5 Retraction Settings Fine-Tuning
Retraction settings are crucial for preventing stringing and oozing, common issues that can ruin print quality. Retraction pulls the filament back into the nozzle when the print head moves between different parts of the model. Fine-tuning these settings is essential for clean and accurate prints.
Retraction Distance and Speed
Retraction distance is the amount of filament retracted, and retraction speed is the speed at which it’s retracted. The ideal retraction distance and speed vary depending on your printer, nozzle, and filament. Start with a retraction distance of 2-3 mm and a retraction speed of 25-35 mm/s. Adjust these settings gradually until you eliminate stringing without causing other issues such as under-extrusion or jams.
Avoiding Stringing and Blobs
Stringing and blobs are common problems that can be addressed by optimizing retraction settings. If you see strings of filament between parts of your print, increase the retraction distance and/or speed. If you notice blobs or excess material on your prints, reduce the temperature slightly and ensure the nozzle is clean.
Troubleshooting Common Printing Issues
Even with the best Slic3r settings, you may encounter printing issues. However, by understanding common problems and their solutions, you can quickly identify and resolve them, ensuring successful prints. Here are some tips to address issues.
Layer Adhesion Problems
Poor layer adhesion can result in a weak or failed print. To address this, ensure your nozzle temperature is correct for your filament, slow down the print speed, and make sure the bed is level. Proper bed leveling is the key here.
Warping and Curling Solutions
Warping and curling often occur with filaments like ABS due to thermal contraction. To minimize warping, use a heated bed, enclose your printer, and ensure good bed adhesion. Using a brim can help a lot with this issue.
Stringing and Oozing Remedies
Stringing and oozing are caused by the filament dripping from the nozzle during travel moves. To fix this, optimize retraction settings, lower the nozzle temperature, and ensure the nozzle is clean. Also make sure that your print head does not get any obstacles while moving.